
Osteoporosis
- Home
- Blog
- Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more susceptible to sudden and unexpected fractures. The disease often progresses without any symptoms or pain, and is not found until bones fracture. You can take steps to prevent this disease, and treatments do exist.
What is osteoporosis?
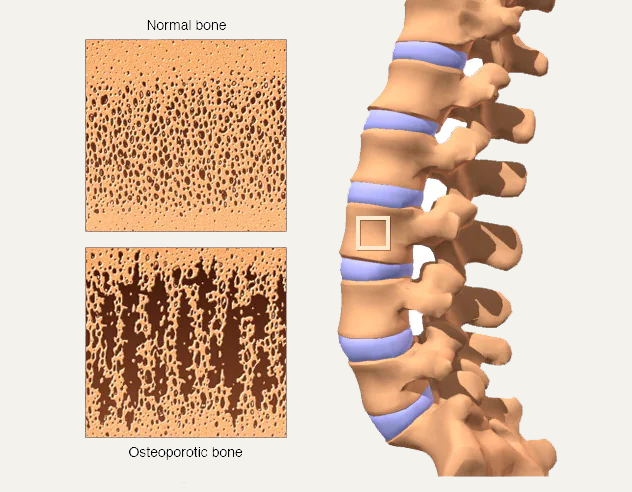
The word ‘osteoporosis’ means ‘porous bone.’ It is a disease that weakens bones, and if you have it, you are at a greater risk for sudden and unexpected bone fractures. Osteoporosis means that you have less bone mass and strength. The disease often develops without any symptoms or pain, and it is usually not discovered until the weakened bones cause painful fractures. Most of these are fractures of the hip, wrist and spine.
Who gets osteoporosis?
After age 50, one in two women and one in four men will have an osteoporosis-related fracture in their lifetimes. Another 30% have low bone density that puts them at risk of developing osteoporosis. This condition is called osteopenia.
What causes osteoporosis?
When osteoporosis occurs, the "holes" in the "sponge" grow larger and more numerous, which weakens the inside of the bone. Bones support the body and protect vital organs. Bones also store calcium and other minerals. When the body needs calcium, it breaks down and rebuilds bone. This process, called bone remodeling, supplies the body with needed calcium while keeping the bones strong.
Up until about age 30, you normally build more bone than you lose. After age 35, bone breakdown occurs faster than bone buildup, which causes a gradual loss of bone mass. If you have osteoporosis, you lose bone mass at a greater rate. After menopause, the rate of bone breakdown occurs even more quickly.
What are the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Usually, there are no symptoms of osteoporosis. That is why it is sometimes called a silent disease. However, you should watch out for the following things:
- Loss of height (getting shorter by an inch or more).
- Change in posture (stooping or bending forward).
- Shortness of breath (smaller lung capacity due to compressed disks).
- Bone fractures.
- Pain in the lower back.
Who is at risk for developing osteoporosis?
There are many risk factors that increase your chance of developing osteoporosis, with two of the most significant being gender and age.
Your risk of developing osteoporosis is also linked to ethnicity. Caucasian and Asian women are more likely to develop osteoporosis. However, African-American and Hispanic women are still at risk. In fact, African-American women are more likely than white women to die after a hip fracture.
Another factor is bone structure and body weight. Petite and thin people have a greater risk of developing osteoporosis because they have less bone to lose than people with more body weight and larger frames.
Family history also plays a part in osteoporosis risk. If your parents or grandparents have had any signs of osteoporosis, such as a fractured hip after a minor fall, you may have a greater risk of developing the disease.
Finally, some medical conditions and medications increase your risk. If you have or had any of the following conditions, some of which are related to irregular hormone levels, you and your healthcare provider might consider earlier screening for osteoporosis.
- Overactive thyroid, parathyroid, or adrenal glands.
- History of bariatric (weight loss) surgery or organ transplant.
- Hormone treatment for breast or prostate cancer or a history of missed periods.
- Celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Blood diseases such as multiple myeloma.
How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
All women over the age of 65 should have a bone density test. The DEXA scan may be done earlier for women who have risk factors for osteoporosis. Men over age 70, or younger men with risk factors, should also consider getting a bone density test.
How is osteoporosis treated?
The treatment option given by best orthopedic doctors at orthopedic hospital in Guntur depends on the severity of the patient’s condition.
In fracture or dislocation of bones splint, cast or braces are used to immobilize the joints or bones. In back pain or arthritis treatments like anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, injection, acupuncture, or in severe cases surgery is prescribed. Get the best fracture treatment by orthopedic surgeon in AP.
In some cases where medication, Physiotherapy is not the solution then surgery is performed by best orthopedic specialist in AP which are
Total Joint Replacement- A prosthesis joint is replaced at the place of the damaged joint.
Arthroscopic surgery- It is used to repair common injuries with several small thin instruments.
Fracture repair- Different implant techniques like a rod, screw, plates, etc. are used to repair the fractured bones.
Bone grafting - Another part of the bone from the patient’s body is used to repair and strengthen the damaged bone.
Spinal Fusion- Adjoining vertebrae of the spine are fused.
